SIPp 是一个短小精悍的脚本工具,可以支持模拟客户端与服务端的模式,对于生产压测、功能测试都有一定帮助。
如何安装?
可以参考官方说明文档,一步步带你安装、了解特性、开始测试
编译好的版本
可以直接在 Github 下载稳定编译好的版本:Github 版本发布页
自己构建
环境和背景条件要求
官方是支持在 Linux和Cygwin(Windows平台上运行的UNIX模拟环境)下可使用,其他环境未经测试,可能可以使用。
此外你需要具备:
- C++ 编译器
- curses or ncurses library
- For TLS 支持: OpenSSL >= 0.9.8 or WolfSSL >= 3.15.0
- For pcap play 支持: libpcap and libnet
- For SCTP 支持: lksctp-tools
- For distributed pauses: Gnu Scientific Libraries
常规如果你不需要支持TLS/SCTP/PCAP 的话,只需要
tar -xvzf sipp-xxx.tar
cd sipp
cmake .
make
4个步骤就可以开启编译
如何使用?
包含的参数属性很多:
# ./sipp --help
/usr/bin/pager: No such file or directory
Usage:
sipp remote_host[:remote_port] [options]
Example:
Run SIPp with embedded server (uas) scenario:
./sipp -sn uas
On the same host, run SIPp with embedded client (uac) scenario:
./sipp -sn uac 127.0.0.1
Available options:
*** Scenario file options:
-sd : Dumps a default scenario (embedded in the SIPp executable)
-sf : Loads an alternate XML scenario file. To learn more about XML scenario
syntax, use the -sd option to dump embedded scenarios. They contain all the
necessary help.
-oocsf : Load out-of-call scenario.
-oocsn : Load out-of-call scenario.
-sn : Use a default scenario (embedded in the SIPp executable). If this option is
omitted, the Standard SipStone UAC scenario is loaded.
Available values in this version:
- 'uac' : Standard SipStone UAC (default).
- 'uas' : Simple UAS responder.
- 'regexp' : Standard SipStone UAC - with regexp and variables.
- 'branchc' : Branching and conditional branching in scenarios - client.
- 'branchs' : Branching and conditional branching in scenarios - server.
Default 3pcc scenarios (see -3pcc option):
- '3pcc-C-A' : Controller A side (must be started after all other 3pcc
scenarios)
- '3pcc-C-B' : Controller B side.
- '3pcc-A' : A side.
- '3pcc-B' : B side.
*** IP, port and protocol options:
-t : Set the transport mode:
- u1: UDP with one socket (default),
- un: UDP with one socket per call,
- ui: UDP with one socket per IP address. The IP addresses must be defined
in the injection file.
- t1: TCP with one socket,
- tn: TCP with one socket per call,
- c1: u1 + compression (only if compression plugin loaded),
- cn: un + compression (only if compression plugin loaded). This plugin is
not provided with SIPp.
-i : Set the local IP address for 'Contact:','Via:', and 'From:' headers. Default
is primary host IP address.
-p : Set the local port number. Default is a random free port chosen by the
system.
-bind_local : Bind socket to local IP address, i.e. the local IP address is used as the
source IP address. If SIPp runs in server mode it will only listen on the
local IP address instead of all IP addresses.
-ci : Set the local control IP address
-cp : Set the local control port number. Default is 8888.
-max_socket : Set the max number of sockets to open simultaneously. This option is
significant if you use one socket per call. Once this limit is reached,
traffic is distributed over the sockets already opened. Default value is
50000
-max_reconnect : Set the the maximum number of reconnection.
-reconnect_close : Should calls be closed on reconnect?
-reconnect_sleep : How long (in milliseconds) to sleep between the close and reconnect?
-rsa : Set the remote sending address to host:port for sending the messages.
*** SIPp overall behavior options:
-v : Display version and copyright information.
-bg : Launch SIPp in background mode.
-nostdin : Disable stdin.
-plugin : Load a plugin.
-sleep : How long to sleep for at startup. Default unit is seconds.
-skip_rlimit : Do not perform rlimit tuning of file descriptor limits. Default: false.
-buff_size : Set the send and receive buffer size.
-sendbuffer_warn : Produce warnings instead of errors on SendBuffer failures.
-lost : Set the number of packets to lose by default (scenario specifications
override this value).
-key : keyword value
Set the generic parameter named "keyword" to "value".
-set : variable value
Set the global variable parameter named "variable" to "value".
-tdmmap : Generate and handle a table of TDM circuits.
A circuit must be available for the call to be placed.
Format: -tdmmap {0-3}{99}{5-8}{1-31}
-dynamicStart : variable value
Set the start offset of dynamic_id variable
-dynamicMax : variable value
Set the maximum of dynamic_id variable
-dynamicStep : variable value
Set the increment of dynamic_id variable
*** Call behavior options:
-aa : Enable automatic 200 OK answer for INFO, NOTIFY, OPTIONS and UPDATE.
-base_cseq : Start value of [cseq] for each call.
-cid_str : Call ID string (default %u-%p@%s). %u=call_number, %s=ip_address,
%p=process_number, %%=% (in any order).
-d : Controls the length of calls. More precisely, this controls the duration of
'pause' instructions in the scenario, if they do not have a 'milliseconds'
section. Default value is 0 and default unit is milliseconds.
-deadcall_wait : How long the Call-ID and final status of calls should be kept to improve
message and error logs (default unit is ms).
-auth_uri : Force the value of the URI for authentication.
By default, the URI is composed of remote_ip:remote_port.
-au : Set authorization username for authentication challenges. Default is taken
from -s argument
-ap : Set the password for authentication challenges. Default is 'password'
-s : Set the username part of the request URI. Default is 'service'.
-default_behaviors: Set the default behaviors that SIPp will use. Possible values are:
- all Use all default behaviors
- none Use no default behaviors
- bye Send byes for aborted calls
- abortunexp Abort calls on unexpected messages
- pingreply Reply to ping requests
- cseq Check CSeq of ACKs
If a behavior is prefaced with a -, then it is turned off. Example:
all,-bye
-nd : No Default. Disable all default behavior of SIPp which are the following:
- On UDP retransmission timeout, abort the call by sending a BYE or a CANCEL
- On receive timeout with no ontimeout attribute, abort the call by sending
a BYE or a CANCEL
- On unexpected BYE send a 200 OK and close the call
- On unexpected CANCEL send a 200 OK and close the call
- On unexpected PING send a 200 OK and continue the call
- On unexpected ACK CSeq do nothing
- On any other unexpected message, abort the call by sending a BYE or a
CANCEL
-pause_msg_ign : Ignore the messages received during a pause defined in the scenario
-callid_slash_ign: Don't treat a triple-slash in Call-IDs as indicating an extra SIPp prefix.
*** Injection file options:
-inf : Inject values from an external CSV file during calls into the scenarios.
First line of this file say whether the data is to be read in sequence
(SEQUENTIAL), random (RANDOM), or user (USER) order.
Each line corresponds to one call and has one or more ';' delimited data
fields. Those fields can be referred as [field0], [field1], ... in the xml
scenario file. Several CSV files can be used simultaneously (syntax: -inf
f1.csv -inf f2.csv ...)
-infindex : file field
Create an index of file using field. For example -inf ../path/to/users.csv
-infindex users.csv 0 creates an index on the first key.
-ip_field : Set which field from the injection file contains the IP address from which
the client will send its messages.
If this option is omitted and the '-t ui' option is present, then field 0 is
assumed.
Use this option together with '-t ui'
*** RTP behaviour options:
-mi : Set the local media IP address (default: local primary host IP address)
-rtp_echo : Enable RTP echo. RTP/UDP packets received on media port are echoed to their
sender.
RTP/UDP packets coming on this port + 2 are also echoed to their sender
(used for sound and video echo).
-mb : Set the RTP echo buffer size (default: 2048).
-min_rtp_port : Minimum port number for RTP socket range.
-max_rtp_port : Maximum port number for RTP socket range.
-rtp_payload : RTP default payload type.
-rtp_threadtasks : RTP number of playback tasks per thread.
-rtp_buffsize : Set the rtp socket send/receive buffer size.
-rtpcheck_debug : Write RTP check debug information to file
-audiotolerance : Audio error tolerance for RTP checks (0.0-1.0) -- default: 1.0
-videotolerance : Video error tolerance for RTP checks (0.0-1.0) -- default: 1.0
*** Call rate options:
-r : Set the call rate (in calls per seconds). This value can bechanged during
test by pressing '+', '_', '*' or '/'. Default is 10.
pressing '+' key to increase call rate by 1 * rate_scale,
pressing '-' key to decrease call rate by 1 * rate_scale,
pressing '*' key to increase call rate by 10 * rate_scale,
pressing '/' key to decrease call rate by 10 * rate_scale.
-rp : Specify the rate period for the call rate. Default is 1 second and default
unit is milliseconds. This allows you to have n calls every m milliseconds
(by using -r n -rp m).
Example: -r 7 -rp 2000 ==> 7 calls every 2 seconds.
-r 10 -rp 5s => 10 calls every 5 seconds.
-rate_scale : Control the units for the '+', '-', '*', and '/' keys.
-rate_increase : Specify the rate increase every -rate_interval units (default is seconds).
This allows you to increase the load for each independent logging period.
Example: -rate_increase 10 -rate_interval 10s
==> increase calls by 10 every 10 seconds.
-rate_max : If -rate_increase is set, then quit after the rate reaches this value.
Example: -rate_increase 10 -rate_max 100
==> increase calls by 10 until 100 cps is hit.
-rate_interval : Set the interval by which the call rate is increased. Defaults to the value
of -fd.
-no_rate_quit : If -rate_increase is set, do not quit after the rate reaches -rate_max.
-l : Set the maximum number of simultaneous calls. Once this limit is reached,
traffic is decreased until the number of open calls goes down. Default:
(3 * call_duration (s) * rate).
-m : Stop the test and exit when 'calls' calls are processed
-users : Instead of starting calls at a fixed rate, begin 'users' calls at startup,
and keep the number of calls constant.
*** Retransmission and timeout options:
-recv_timeout : Global receive timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If the expected message
is not received, the call times out and is aborted.
-send_timeout : Global send timeout. Default unit is milliseconds. If a message is not sent
(due to congestion), the call times out and is aborted.
-timeout : Global timeout. Default unit is seconds. If this option is set, SIPp quits
after nb units (-timeout 20s quits after 20 seconds).
-timeout_error : SIPp fails if the global timeout is reached is set (-timeout option
required).
-max_retrans : Maximum number of UDP retransmissions before call ends on timeout. Default
is 5 for INVITE transactions and 7 for others.
-max_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for invite transactions before call
ends on timeout.
-max_non_invite_retrans: Maximum number of UDP retransmissions for non-invite transactions before call
ends on timeout.
-nr : Disable retransmission in UDP mode.
-rtcheck : Select the retransmission detection method: full (default) or loose.
-T2 : Global T2-timer in milli seconds
*** Third-party call control options:
-3pcc : Launch the tool in 3pcc mode ("Third Party call control"). The passed IP
address depends on the 3PCC role.
- When the first twin command is 'sendCmd' then this is the address of the
remote twin socket. SIPp will try to connect to this address:port to send
the twin command (This instance must be started after all other 3PCC
scenarios).
Example: 3PCC-C-A scenario.
- When the first twin command is 'recvCmd' then this is the address of the
local twin socket. SIPp will open this address:port to listen for twin
command.
Example: 3PCC-C-B scenario.
-master : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the master number
-slave : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the slave number
-slave_cfg : 3pcc extended mode: indicates the file where the master and slave addresses
are stored
*** Performance and watchdog options:
-timer_resol : Set the timer resolution. Default unit is milliseconds. This option has an
impact on timers precision.Small values allow more precise scheduling but
impacts CPU usage.If the compression is on, the value is set to 50ms. The
default value is 10ms.
-max_recv_loops : Set the maximum number of messages received read per cycle. Increase this
value for high traffic level. The default value is 1000.
-max_sched_loops : Set the maximum number of calls run per event loop. Increase this value for
high traffic level. The default value is 1000.
-watchdog_interval: Set gap between watchdog timer firings. Default is 400.
-watchdog_reset : If the watchdog timer has not fired in more than this time period, then reset
the max triggers counters. Default is 10 minutes.
-watchdog_minor_threshold: If it has been longer than this period between watchdog executions count a
minor trip. Default is 500.
-watchdog_major_threshold: If it has been longer than this period between watchdog executions count a
major trip. Default is 3000.
-watchdog_major_maxtriggers: How many times the major watchdog timer can be tripped before the test is
terminated. Default is 10.
-watchdog_minor_maxtriggers: How many times the minor watchdog timer can be tripped before the test is
terminated. Default is 120.
*** Tracing, logging and statistics options:
-f : Set the statistics report frequency on screen. Default is 1 and default unit
is seconds.
-trace_stat : Dumps all statistics in <scenario_name>_<pid>.csv file. Use the '-h stat'
option for a detailed description of the statistics file content.
-stat_delimiter : Set the delimiter for the statistics file
-stf : Set the file name to use to dump statistics
-fd : Set the statistics dump log report frequency. Default is 60 and default unit
is seconds.
-periodic_rtd : Reset response time partition counters each logging interval.
-trace_msg : Displays sent and received SIP messages in <scenario file
name>_<pid>_messages.log
-message_file : Set the name of the message log file.
-message_overwrite: Overwrite the message log file (default true).
-trace_shortmsg : Displays sent and received SIP messages as CSV in <scenario file
name>_<pid>_shortmessages.log
-shortmessage_file: Set the name of the short message log file.
-shortmessage_overwrite: Overwrite the short message log file (default true).
-trace_counts : Dumps individual message counts in a CSV file.
-trace_err : Trace all unexpected messages in <scenario file name>_<pid>_errors.log.
-error_file : Set the name of the error log file.
-error_overwrite : Overwrite the error log file (default true).
-trace_error_codes: Dumps the SIP response codes of unexpected messages to <scenario file
name>_<pid>_error_codes.log.
-trace_calldebug : Dumps debugging information about aborted calls to
<scenario_name>_<pid>_calldebug.log file.
-calldebug_file : Set the name of the call debug file.
-calldebug_overwrite: Overwrite the call debug file (default true).
-trace_screen : Dump statistic screens in the <scenario_name>_<pid>_screens.log file when
quitting SIPp. Useful to get a final status report in background mode (-bg
option).
-screen_file : Set the name of the screen file.
-screen_overwrite: Overwrite the screen file (default true).
-trace_rtt : Allow tracing of all response times in <scenario file name>_<pid>_rtt.csv.
-rtt_freq : freq is mandatory. Dump response times every freq calls in the log file
defined by -trace_rtt. Default value is 200.
-trace_logs : Allow tracing of <log> actions in <scenario file name>_<pid>_logs.log.
-log_file : Set the name of the log actions log file.
-log_overwrite : Overwrite the log actions log file (default true).
-ringbuffer_files: How many error, message, shortmessage and calldebug files should be kept
after rotation?
-ringbuffer_size : How large should error, message, shortmessage and calldebug files be before
they get rotated?
-max_log_size : What is the limit for error, message, shortmessage and calldebug file sizes.
Signal handling:
SIPp can be controlled using POSIX signals. The following signals
are handled:
USR1: Similar to pressing the 'q' key. It triggers a soft exit
of SIPp. No more new calls are placed and all ongoing calls
are finished before SIPp exits.
Example: kill -SIGUSR1 732
USR2: Triggers a dump of all statistics screens in
<scenario_name>_<pid>_screens.log file. Especially useful
in background mode to know what the current status is.
Example: kill -SIGUSR2 732
Exit codes:
Upon exit (on fatal error or when the number of asked calls (-m
option) is reached, SIPp exits with one of the following exit
code:
0: All calls were successful
1: At least one call failed
97: Exit on internal command. Calls may have been processed
99: Normal exit without calls processed
253: RTP validation failure
-1: Fatal error
-2: Fatal error binding a socket
About server
如何启动服务端,开启一个UAS
./sipp -sf example-server.xml -i host -p port --max_socket 100000 -l 500000
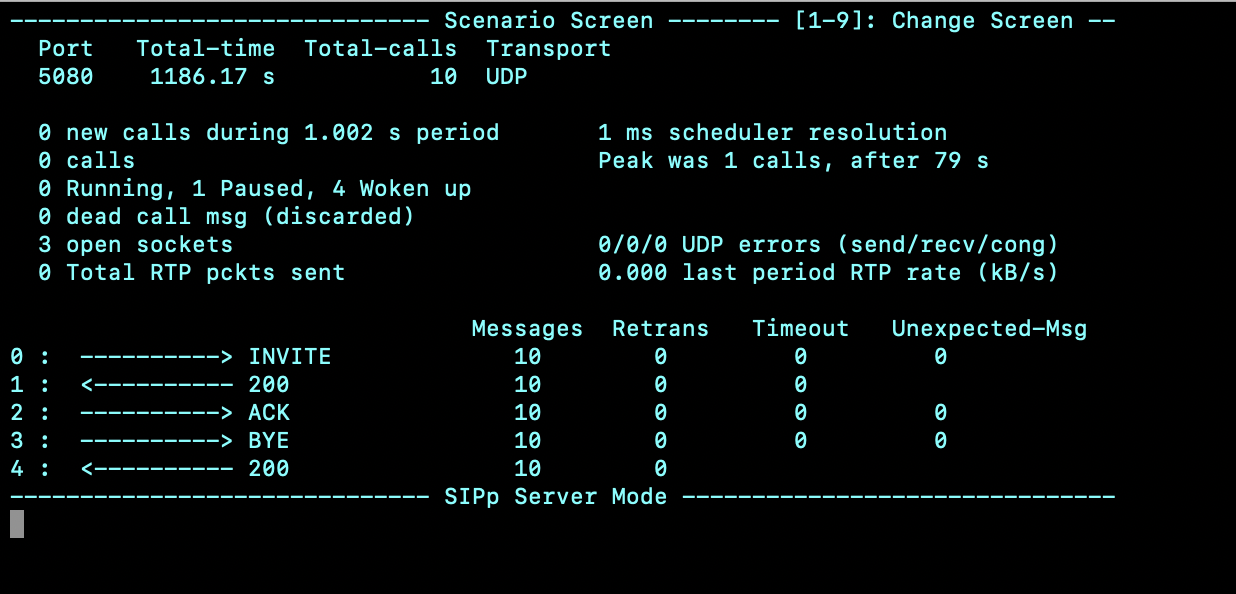
服务端脚本一般如何设计:
一般根据实际生产情况,存在client-bye, server-bye, server-rejected, client-cancel, server-cancel等多种情况 以下展示最为常见的主叫挂断:client-bye,即被叫服务侧需要能够接受客服端的bye指令,并回复200ACK
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<scenario name="Basic UAS scenario">
<recv request="INVITE">
<action>
<ereg regexp="sip:(.*)>.*" search_in="hdr" header="Contact" assign_to="trash"/>
</action>
</recv>
<!-- since SIPp complains about not used variable reference the trach var -->
<Reference variables="trash"/>
<send retrans="500">
<![CDATA[
SIP/2.0 200 OK
[last_Via:]
[last_From:]
[last_To:];tag=[pid]SIPpTag01[call_number]
[last_Call-ID:]
[last_CSeq:]
Contact: <sip:[local_ip]:[local_port];transport=[transport]>
Content-Type: application/sdp
Content-Length: [len]
v=0
o=user1 53655765 2353687637 IN IP[local_ip_type] [local_ip]
s=-
c=IN IP[media_ip_type] [media_ip]
t=0 0
m=audio [media_port] RTP/AVP 0
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
]]>
</send>
<recv request="ACK">
</recv>
<recv request="BYE">
</recv>
<send>
<![CDATA[
SIP/2.0 200 OK
[last_Via:]
[last_From:]
[last_To:]
[last_Call-ID:]
[last_CSeq:]
Contact: <sip:[local_ip]:[local_port];transport=[transport]>
Content-Length: 0
]]>
</send>
</scenario>
- 收到 INVITE 回200
- 收到 ACK
- 收到 BYE 回200
About client
如何启动服务端,开启一个UAC
指定送往的代理地址,指定并发量,指定总量级,指定被叫(含前缀)
./sipp proxyhost:port -sf example-client.xml -r batchsize -d 10000 -s caller -m totalcount
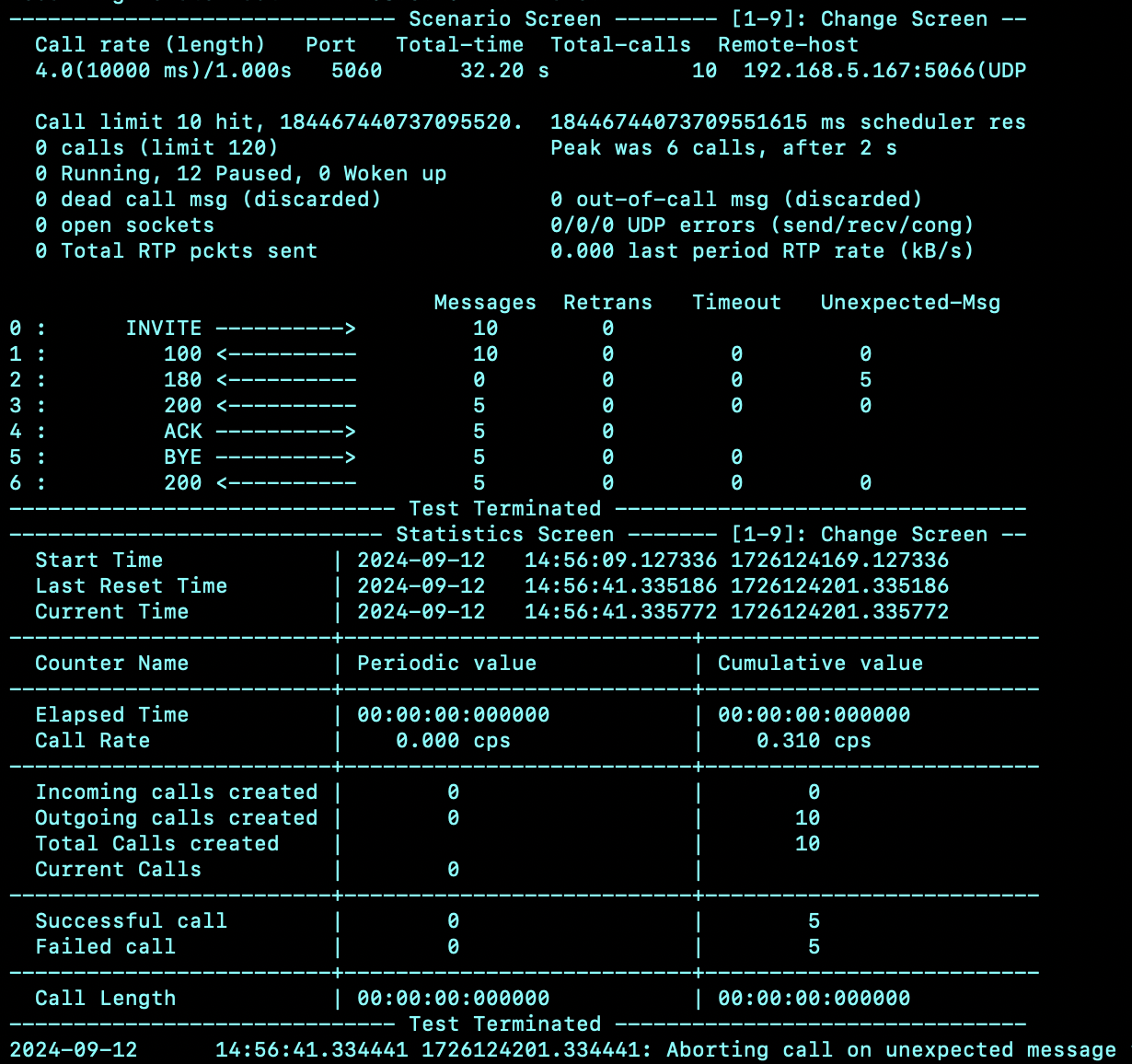
对于客户端的脚本,通常要与服务端对应,也可以模拟一些异常情况,随机回复到异常的情况,比如呼叫后取消、呼叫后保持、呼叫后挂起一段时间等
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<scenario name="Basic UAC scenario">
<send>
<![CDATA[
INVITE sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port] SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/[transport] [local_ip]:[local_port]
From: sipp <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>;tag=[call_number]
To: sut <sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port]>
Call-ID: [call_id]
Cseq: 1 INVITE
Contact: <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>
Content-Type: application/sdp
Content-Length: [len]
v=0
o=user1 53655765 2353687637 IN IP[local_ip_type] [local_ip]
s=-
t=0 0
c=IN IP[media_ip_type] [media_ip]
m=audio [media_port] RTP/AVP 0
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
]]>
</send>
<recv response="100" optional="true">
</recv>
<recv response="180" optional="true">
</recv>
<recv response="200">
</recv>
<send>
<![CDATA[
ACK sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port] SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/[transport] [local_ip]:[local_port]
From: sipp <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>;tag=[call_number]
To: sut <sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port]>[peer_tag_param]
Call-ID: [call_id]
Cseq: 1 ACK
Contact: <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>
Content-Length: 0
]]>
</send>
<send retrans="500">
<![CDATA[
BYE sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port] SIP/2.0
Via: SIP/2.0/[transport] [local_ip]:[local_port]
From: sipp <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>;tag=[call_number]
To: sut <sip:[service]@[remote_ip]:[remote_port]>[peer_tag_param]
Call-ID: [call_id]
Cseq: 2 BYE
Contact: <sip:sipp@[local_ip]:[local_port]>
Content-Length: 0
]]>
</send>
<recv response="200">
</recv>
</scenario>
- 发送 INVITE
- 等待100、180的可选指令 ,200 的必要指令
- 收到200后,发送 ACK
- 而后发出 BYE指令,最终等待200返回
About testcase
根据以上描述的内容,需要构建好双端的测试脚本,生产情况需要覆盖尽可能多的业务场景,压测情况可以采用正常来回的脚本
successful call bye from client
./sipp -sf uas.xml -i host -p port --max_socket 100000 -l 500000
./sipp proxyhost:port -sf uac.xml -r 5 -d 10000 -s 20240715 -m 5
正常先开启服务端,再启动客户端,根据代理的能力,服务端可以多端口多开